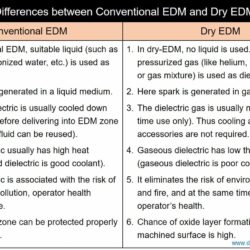
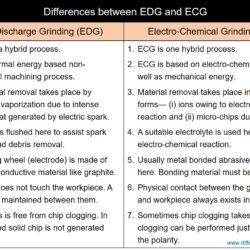
Difference Between USM and EDM – Ultrasonic Machining & Electric Discharge Machining
Machining is one type of subtractive manufacturing processes where excess material is removed from the workpiece to produce intended feature. Conventional machining processes (such as turning, threading, facing, milling, shaping, drilling, hobbing, etc.) employ a wedge-shaped cutting tool to shear off the workpiece material in the form of chips. Such processes always utilize mechanical energy in order to remove material by shearing. Several non-conventional machining processes have also emerged over