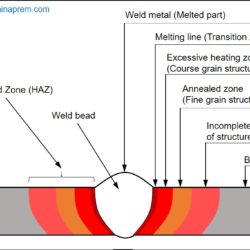
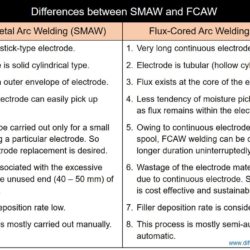
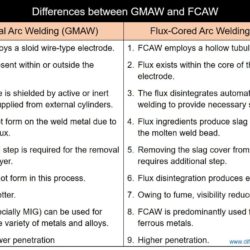
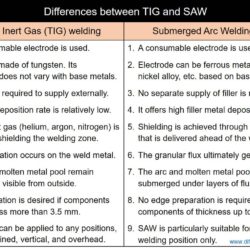
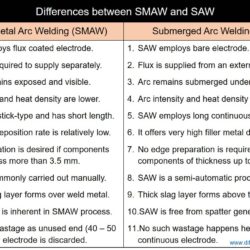
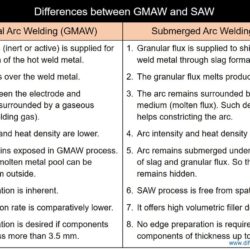
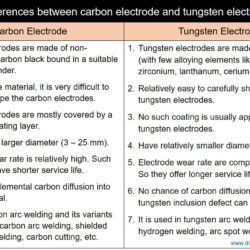
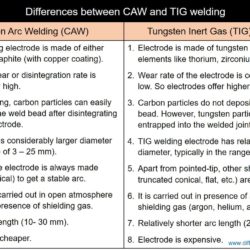
Difference Between Weld Metal and Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
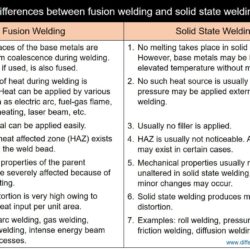
Welding is one of the manufacturing processes where two or more materials can be joined permanently through coalescence formation with or without the application of external heat, pressure, or filler metal. Welding processes can be broadly classified as fusion welding and solid state welding. In fusion welding processes, significant amount of heat (thermal energy) is applied from external source in order to fuse (melt) the faying surfaces of the components