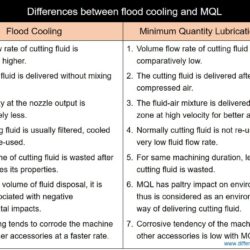
Difference Between Coolant and Lubricant as Cutting Fluid in Machining
During conventional machining or metal cutting, excess material is gradually removed from the workpiece in the form of chips using a wedge shaped cutting tool. Primarily due to continuous rubbing between moving chips and rake surface of cutting tool, intense heat is generated at the cutting zone. In continuous machining, this cutting heat leads to increase in temperature at the cutting zone. Excessive cutting temperature has several detrimental effects on