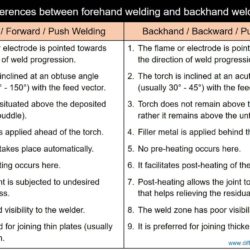
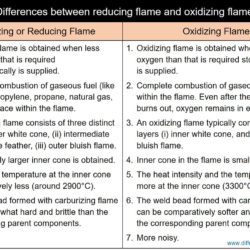
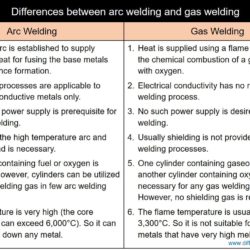
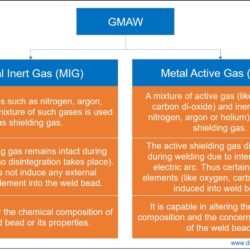
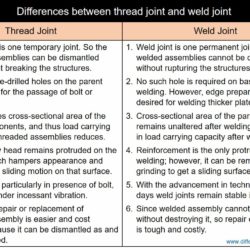
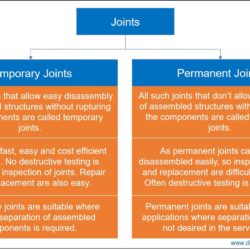
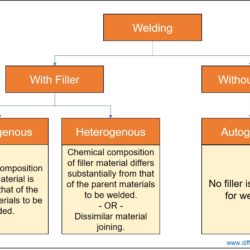
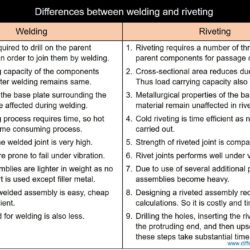
Difference Between Forehand Welding and Backhand Welding
In gas welding, a flame supplies necessary heat for fusing the base metals. Similarly, in arc welding, an electric arc supplies necessary heat. While joining two components by either gas welding or arc welding, the flame or arc can be moved towards the direction of weld progression or opposite to the direction of weld progression. Based on the relative position of the weld bead (puddle) and flame/arc, welding technique can