Gear drive is most widely used mechanical power transmission system in small to large scale machineries. It is one engagement type positive drive (no slip) suitable for transmitting motion, torque and power over comparatively small distances (usually below 1 m) and also modifying them as per requirement. Power is transferred from driving shaft to driven shaft by means of successive engagement and disengagement of teeth cut on the cylindrical gear blank. Different type of gears have different teeth arrangement. For example, spur gear has straight teeth that are parallel to the gear axis. In case of helical gear, teeth are cut in the form of helix on the pitch cylinder of the gear blank. Although spur gear and helical gear both are used for transmitting power between parallel shafts only, helical teeth offers numerous benefits such as higher load carrying capacity, low vibration, low noise, less wear rate and prolonged life. However, a pair of mating helical gears impose axial load on the bearings along with radial force.
This detrimental axial force can, however, be eliminated by employing two identical helical gears having same module and number of teeth and are joined on same axis but having teeth in opposite directions (one has left hand helix and other one has right hand helix). Such a helical gear arrangement is termed as double helical gear. Here, thrust force developed by each of the helical gears is opposite in direction but same in magnitude, and thus resultant thrust load becomes zero. It is worth mentioning that double helical gear and herringbone gear are used interchangeably, they are not exactly same, at least from construction and manufacturing points of view. Various similarities and differences between single helical gear and double helical gear are given below in table form.
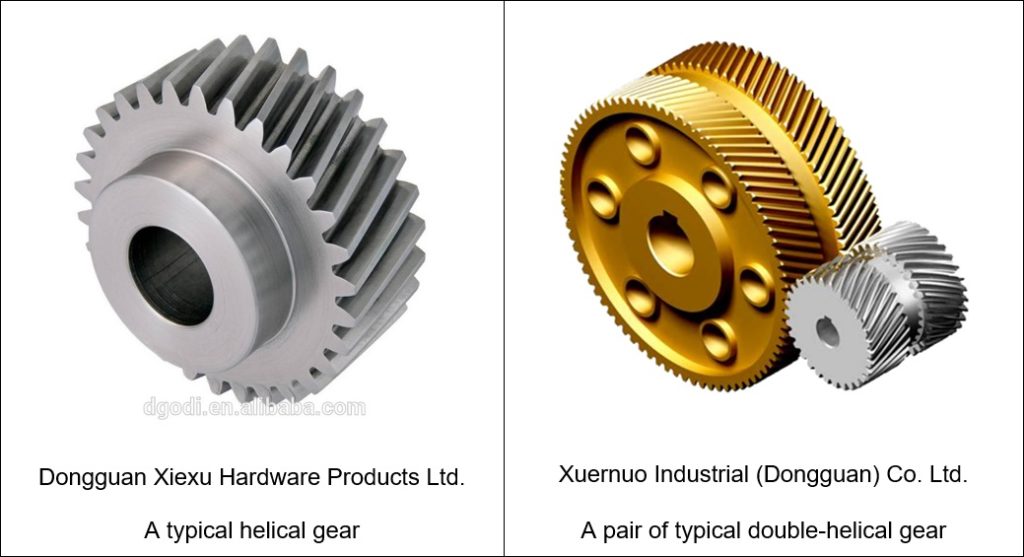
Similarities between single helical gear and double helical gear
- Like every gear drive, these two are also engagement type mechanical drives. A chain drive is another example for the same. Though belt drive is one mechanical drive, it is one friction drive.
- In both the cases teeth are cut in the form of helix on the pitch cylinder of the gear blank. Hand of helix is, however, different for two cases.
- In both the cases teeth of two mating gears come in contact gradually. Thus vibration, noise and teeth wear rate reduce substantially as compared to spur gear.
- Both are applicable for transmitting motion and power between parallel shafts only. A bevel gear can be used for transmitting power between intersecting shafts, while worm gear can be employed for non-intersecting non-parallel shafts.
Differences between single helical gear and double helical gear
| Single Helical Gear | Double Helical Gear |
|---|---|
| A single helical gear has teeth inclined in any one direction (either left hand helix or right hand helix). | Double helical gear consists of two identical gears jointed on same axis, and having teeth in opposite directions (one has left hand helix and other one has right hand helix). |
| Single helical gears develop axial thrust force and exerts the same on corresponding bearings. It also develops radial force. | Resultant thrust force developed in double helical gear is zero. Thus it exerts no axial load on bearings. But radial force exists as usual. |
| Power transmission capacity of single helical gear is comparatively low. | For same size and module, double helical gears can transmit larger power. |
| Single helical gears are cheaper. | Double helical gears are costlier as design and fabrication are difficult and time consuming. |
| High precision is usually not desired during alignment of the gears. | Two helical gears must be aligned precisely otherwise thrust force will not balance properly and the consequence will be unfavorable vibration. |
| Because of thrust load, high helix angle cannot be used. Helix angle for single helical gear usually varies within 15º – 20º. | Due to canceled thrust load, high helix angle (20º – 45º) can be advantageously used in double helical gears. |
| Efficiency of single helical gear is comparatively low. | Double helical gears can provide higher efficiency. |
| Bearing span (distance between two bearings) is short. | Bearing span is longer due to presence of center relief groove in between two gears. |
| Single helical gears are suitable for mechanical drives or power transmission requirements where each application usually requires a unique design for powers, speeds, and configuration. | Double helical gears are suitable for high power transmission requirements such as in cranes, marine drives or turbines. |
References
- Introduction to Machine Design by V. B. Bhandari (McGraw Hill Education India Private Limited).
- Single vs. double helical gears by J. B. Amendola (2 Artec Machine Systems, October 2006. Featured in the Turbomachinery Magazine). artec-machine.com