Geometry of the cutting tool is one crucial factor that influences overall performance (machinability) as well as productivity of machining. Thus cutting tool must be selected judiciously prior to machining based on the work material and cutting conditions. Tool signature displays various features of a cutting tool, and thus it enables quick selection of a cutting tool for specific application. There are several standard systems for designation of a single point turning tool; each displays certain features (like angles and radius) of the cutting tool. Few commonly used systems are— American Standards Association (ASA) system, Orthogonal Rake System (ORS), Normal Rake System (NRS) and Master Rake System (MRS). A same tool may have different tool signatures based on the system of designation followed to specify.
ORS System and NRS System of turning tool designation are sometime confusing as several similarities exist between them even though they are not exactly same. The ORS system employed the orthogonal plane (πO), which is a plane perpendicular to the fixed reference plane. Thus it displays orthogonal rake angle and orthogonal clearance angle in relevant tool signature. ORS system is the most popular one as majority of analysis is carried out considering orthogonal machining (i.e. chip flowing in orthogonal direction). On the other hand, NRS system employs a normal plane (πN), which is plane perpendicular to the cutting edge of the tool. The angle between normal plane and orthogonal plane is nothing but the inclination angle (λ). Thus these two planes coincide when inclination angle becomes zero. Accordingly, ORS and NRS becomes same for a cutting tool having zero inclination angle (λ). Tool signatures along with the name of various features used in these two systems are depicted below. Similarities and differences between these two systems of tool designation are also elaborated in the following sections.
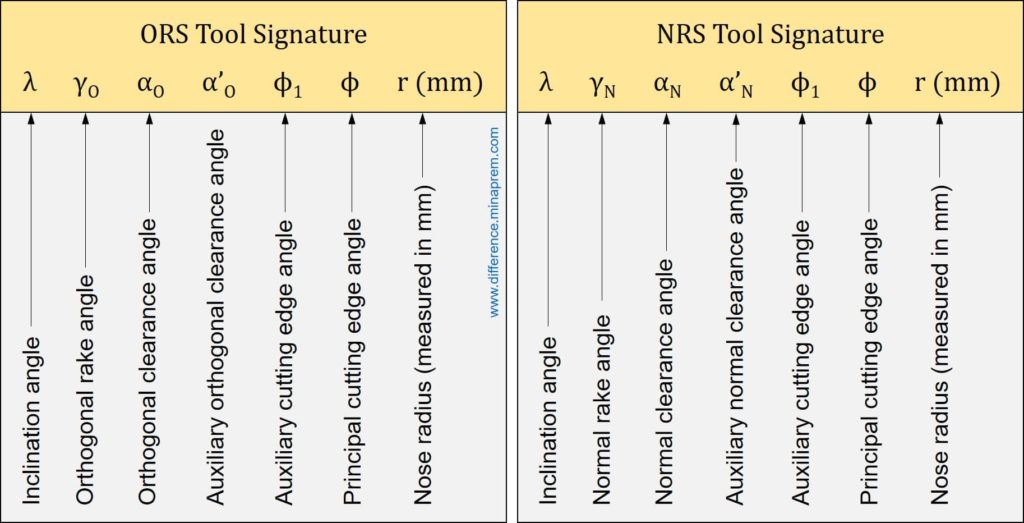
Similarities between ORS and NRS systems
- Both systems are conventionally used for designating turning tools; however, ORS system is more frequently used.
- Both systems specify few common features in the corresponding tool signatures. Such common features include inclination angle, principal cutting edge angle, auxiliary cutting edge angle and nose radius of the cutting tool.
- Both systems specify nose radius value in millimeter (mm). This is unlike ASA system where nose radius is expressed in inch.
- Two planes namely Reference plane and Cutting plane are also common in both systems.
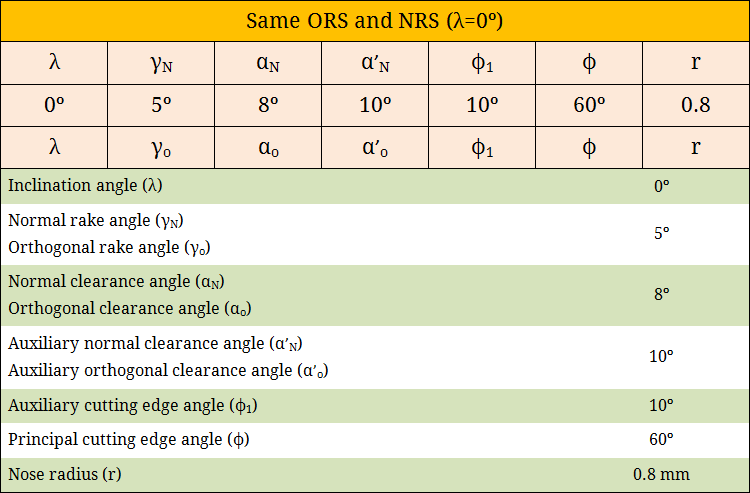
- Angle between Orthogonal plane (used in ORS) and Normal plane (used in NRS) is equal to the inclination angle (λ). So when λ becomes 0º then two planes coincide. Accordingly, ORS system and NRS system becomes exactly same if the cutting tool has zero inclination angle (λ = 0º).
Differences between ORS and NRS systems
| ORS system | NRS system |
|---|---|
| ORS stands for Orthogonal Rake System. | NRS stands for Normal Rake System. |
| It is the ISO old system of turning tool designation. So this system is no more used as an ISO standard. | It is the ISO new system of turning tool designation, and thus is currently used as international standard. |
Three planes used as reference in ORS system are:
|
Three planes used as reference in NRS system are:
|
| These three planes are always mutually perpendicular. | Three planes are not necessarily mutually perpendicular. It will be perpendicular only when inclination angle (λ) is zero. |
| Tool signature in ORS does not reveal true picture if inclination angle λ ≠ 0º. | Tool signature in NRS reveals true picture irrespective of λ value. |
| If ORS system is used while mounting the tool in 3-D vice for re-sharpening it by grinding then additional calculations for angle correction are required. | No such corrections are required if NRS system is used for re-sharpening purpose. Values as per tool signature in NRS are sufficient for accurate mounting in a 3-D vice. |
References
- Machining and Machine Tools by A. B. Chattopadhyay (Wiley).
- Metal Cutting: Theory And Practice by A. Bhattacharya (New Central Book Agency).