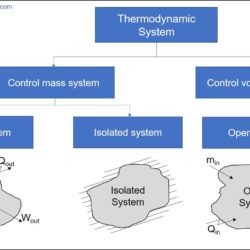
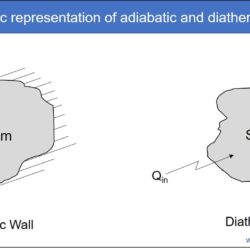
Difference Between Heat and Temperature
Energy may exist in different forms. It can be light energy, thermal energy, potential energy, kinetic energy, chemical energy, nuclear energy, etc. Every physical matter (or body or thermodynamic system) intrinsically possesses certain amount of energy in one form or another. Such energy can be converted from one form to another for storing it within the same body. It can also be transferred from one body to another with or